On-page SEO is the first line of attack when it comes to ranking your website in Google, Yahoo and Bing. Properly optimizing your pages and content can lead to the quickest ROI for the amount of time and energy spent. In this article, you will learn about on-page SEO and how to properly optimize for websites.

Image source: Reliablesoft
What is On-Page SEO?
On-page, also known as on-site, SEO mostly focuses on optimizing the content in the main HTML tags of a page that search engines read to interpret content.
Importance of On-Page SEO
You might have heard that traditional on-page SEO doesn't make a difference to your SEO efforts in 2021.
However, according to Google, in their "How Search Algorithms Work" report, factors such as keyword usage in headings are still used to determine the relevance of a website to a specific search query.
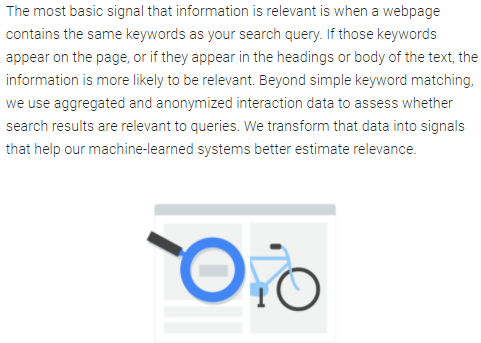
Even with all of Google's modern algorithms, on-page SEO basics still play a major role in getting your website and content to rank in the SERPs.
There's plenty of data to prove it.
Backlinko analyzed 11.8 million Google search results and found that there is a clear correlation between keyword-rich title tags and first-page rankings.
Don't believe the research?
Just simply search for a competitive keyword and you'll find that the top-ranking pages all have the exact keyword in their title tags.
You should note that this optimization process is more than just optimizing keywords and title tags, other factors such as image optimization, SEO-friendly URLs, and fast page speed play an important role in optimizing your website's on-page SEO.
Difference Between On-Page and Off-Page SEO
This is probably one of the most commonly asked questions by many who get started in SEO. And it is important to know the difference between the two.

Image source: SEO Chatter
On-page SEO is all about the optimization of your content, meta tags and links on your web page(s), it’s basically the optimization of everything that is on your website and that is within your control.
Off-page SEO is all about the optimization of external page ranking factors that are not on your website.
Common off-page SEO ranking factors include the following:
- Backlinks from other websites
- Social signals
- Domain authority
- Local SEO optimization on sites such as Yelp, Google My Business and other review sites.
In short, off-page optimization is related to factors that are “off” of your website and on-page optimization is related to factors that are “on” your website.
According to DigitalThirdCoast:
“On-page SEO will determine what search queries you will rank for, whereas off-page SEO will largely determine how high you rank in the SERPs.”
On-Page SEO Ranking Factors and How to Improve Them
Optimize Content
We know that content is one of the most important, if not the most important, aspects of on-page SEO. So when you’re starting with on-page optimization, it would be beneficial to begin with content optimization first.
What is content optimization?
According to Campaign Monitor, content optimization is:
“Content optimization is the process of making sure content is written in a way that it can reach the largest possible target audience.”
Keyword usage is the first thing you should consider when optimizing content.
But how do you know which keywords to use in your content?
Well, before thinking of where and how often to use keywords, you should start by doing keyword research in order to determine which keywords to use.
The golden rule with keyword research is to find keywords that have got a lot of search volume, but very low competition.
You can use a tool such as Ahrefs or SEMrush to conduct some keyword research before you continue optimizing your on-page content.
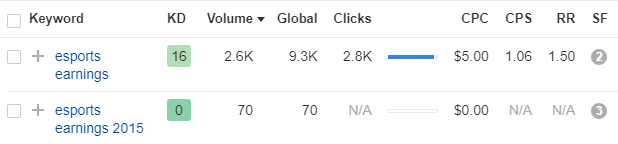
For example, according to Ahrefs, the competition for the keyword “esports league” is really high, so that’s a keyword you want to avoid targeting.
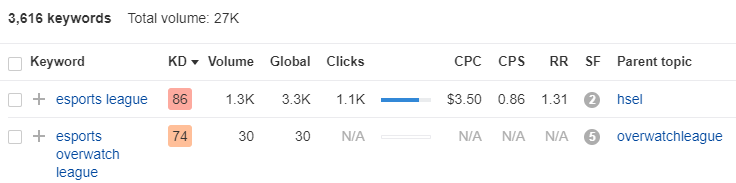
But a keyword like “esports earnings” is definitely one you should be targeting since it’s got low competition and some really high search volume.
This takes us to our next topic - using keywords early.
Use Target Keywords Early
There is an old-school on-page SEO tactic that states that you should use your target keyword once in the first 100 words of your article.
For example, we added the keyword “SEO books” in the first 100 words of our article about The 15 Best SEO Books to Master SEO in 2021:
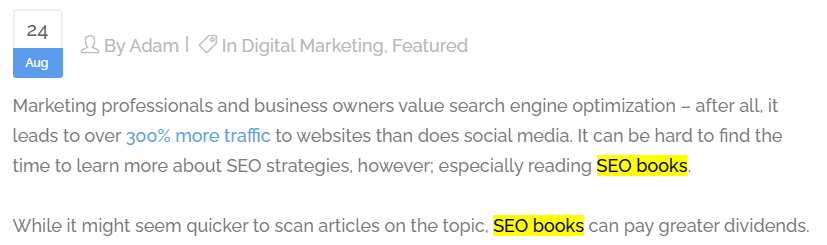
The reason for this is that Google puts more emphasis on the keywords that show up within the first 100 words of your content. Dropping your main keyword within the first 100 words will help Google to understand what your content is about.
Keyword Frequency
You probably know that you should be using your main keyword and variations thereof throughout your content.
But how frequently should you be using your target keywords in your content?
One thing you really want to avoid doing is "keyword stuffing" - the process of stuffing a page with the same keyword in an attempt to manipulate a website's search rankings.
You just simply want to be using your target keyword at different places within your entire article, without trying to sound spammy.
There is not a specific number of times that you should be using a keyword. The golden rule is that it should just be used naturally a few times throughout the text of your article.
Some SEO professionals agree that the target keyword (and variations thereof) should be used no more than once per 200 words of blog copy.
But instead of focusing on how many times to use the target keyword, you should rather place an emphasis on the user experience. When it comes to SEO, you should always consider the user experience.
Using a specific keyword too often in your content will make it difficult to read and will negatively affect the user experience.
To combat this you can make use of a concept called “keyword clustering”. Keyword clustering simply entails creating a group of related keywords that share the same search intent.
So instead of only using one specific keyword in your content, you can make use of or add keywords that are similar.
For example, instead of only targeting “running shoes”, you can add variations of this keyword such as “best running shoes”, “nike running shoes”, “shoes for women”, etc.
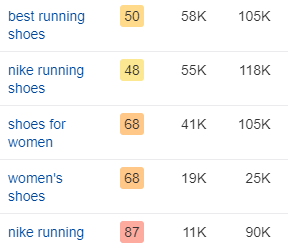
Keyword clustering has several benefits:
- You can rank for long-tail variations of your target keyword
- It avoids excessive use of one specific keyword
- It creates internal linking opportunities
- More organic traffic
Use the Appropriate Heading Tags: h1, h2, etc.
Headings make a website and blog content easier and more enjoyable to read, header tags also simply make the content more organized. Think of them like road signs that guide the user through your content, from the start to the end.

Image source: SkillfulSEO
Did you know that there are 6 different header tags, ranging from H1 down to H6?
Not only do header tags give information about what the content and/or webpage is about, but HTML header tags also create a pleasant user experience. This is because header tags subdivide your content into logical paragraphs, making them easier on the eyes.
I mean, just imagine reading an entire book without chapters! It would be very difficult to read and you’d probably stop reading after a few pages because of the lack of structure. The same could be said of headers in a blog article.
Remember, you want to create content that is user-friendly because user-friendly articles perform well in search engines.
So then, which header tags should you use in your content and where should you use each one?
The H1 Tag
The H1 tag is sometimes referred to as the most important tag on a webpage.
The H1 tag is usually the most visible content on a page and should not be used more than once per page or blog content. Most modern Content Management Systems such as WordPress and Wix, create the blog article title using the H1 tag.
H1 tags can be easily identified on a website:
Or in the page source:
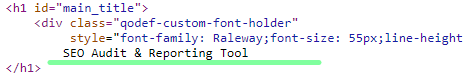
The H2 Tag
The H2 tag is useful for dividing long pieces of text into smaller subsections. This makes the H2 tag useful because it contributes towards creating a good on-page user experience.
Say for example that you’re creating a blog article about “Best Dinner Recipes To Try Out This Summer”, you can subdivide your content into different sections like “Vegetarian Recipes”, “Chicken Recipes”, etc., using the H2 tag.
H3 to H6 Header Tags
The remainder of the header tags should be used to further subdivide the sections you created using the H2 tags.
Let’s go with the previous example, you could use H3, H4, H5 and H6 header tags to create sections about different recipes for each of the categories:
H1: Best Dinner Recipes To Try Out This Summer
H2: Chicken Recipes
H3: Chicken Salad
H4: Classic Chicken Salad
H4: Keto Chicken Salad
H3: Lemon Pepper Chicken
H3: Greek Chicken Pasta
How regularly should you use heading tags in your content?
According to Yoast, a very popular SEO plugin for WordPress, you should be using headings and/or subheadings for every 300 to 350 words of text.
Make Sure Content Satisfies Search Intent
We know the saying, “Content is king.” and yes, good content can do very well in the search engines. But you’ve got to make sure that the content you’re producing satisfies search intent.
How can you check search intent?
Checking search intent for a keyword is easy. All you’ve got to do is type in the keyword that you’re targeting and do an analysis of the content that is currently ranking.
Are all the results on the first page of Google blog articles or are they product-focused? Does Google prioritize local business listings in the Google Map Pack or does the SERP show only blog articles?
A quick analysis of the SERPs will reveal what type of content Google prefers to show users. And obviously, the content that ranks on the first page of Google satisfies search intent, why else would that content rank so well?

Image source: Econsultancy
Optimize Title and Meta Description Tags
It’s important that you create SEO-friendly titles and descriptions for your blog content.
Title Tag
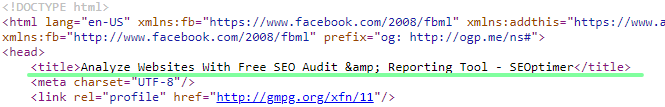
The HTML title tag gives webmasters the ability to give any webpage a name or as the name suggests, a title. A website or page’s title tag can be found in the SERPs or in the browser title bar.
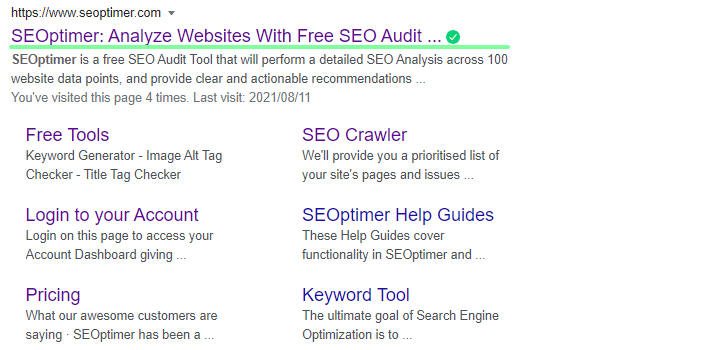
You can also find the title tag of any website by viewing the page source in the browser:
Title tags are still relevant in helping with your search rankings. Moz also states that after content, title tags are the second most important on-page SEO ranking factor.
Furthermore, Google recently announced a new system of generating titles for search engine results. This new system dynamically generates search results titles based on a number of on-page factors.
“We consider the main visual title or headline shown on a page, content that site owners often place within <H1> tags, within other header tags, or which is made large and prominent through the use of style treatments.”
What impact does this have on how you create titles for your content and web pages?
From what we’ve gathered from Google is that you don’t have to worry too much about this update. Just keep focusing on creating good page titles.

How to Create Good Page Titles
Creating good title tags will boost your on-page SEO efforts significantly, here are a few ways to create the perfect page titles.
Use the target keyword at the front of the title tag
The title tag gives both people and search engines an overview of what your content is about. That’s why it’s so important to spend some time creating the perfect title for your content and web pages.
A common practice is to use the target keyword as close to the beginning of the title tag as possible. The closer your target keyword or phrase is to the start of the title, the better.
Just have a look at the top search results, you will see that the target keyword is usually at the start or very near to the beginning of the title:
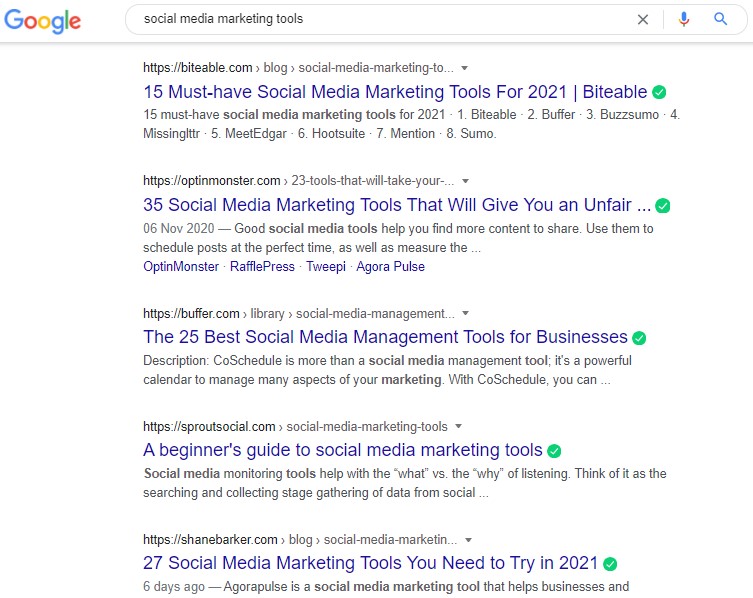
And if the top brands and sites are doing it, then it means that this trick obviously works and that you should implement it too.
Keep title tags short and easy to understand
If your title tag is too long, then the search engines will cut off your page titles in the SERPs. You want readers to be able to see the entire title tag so that they’ve got a clear understanding of what the content is about.
Furthermore, short and simple titles are easier to read and understand. A good title length is anything between 60 to 70 characters, Google may cut off anything longer than that.
Here are some more best practices from Google themselves on how to create good titles for on-page SEO:
- Always avoid keyword stuffing
- Create titles that are descriptive
- Brand your titles
- Avoid using the same title tag more than once
Add title tag modifiers
Another simple trick that you can use to create good titles is by adding title tag modifiers.
Examples of title tag modifiers are “best”, “review”, “free”, “ultimate” and “guide”. By adding title tag modifiers you increase the possibilities of ranking for long-tail keywords.
Another title tag modifier that you can add to your title tags is the year. For example, “15 Must-Have Best Social Media Marketing Tools for 2021.
Use Creative, Keyword-Optimized Meta Descriptions
Meta descriptions are those small pieces of text that can be found below the title on the search engine results page.
These tags appear in a page’s source code and they tell search engine crawlers and readers what the page is about.
Here is an example of the SEOptimer meta description that can be found on the search engine results page:
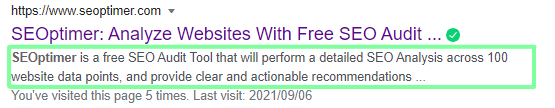
While the meta description may not be as important as the page title when it comes to improving your on-page SEO rankings, these short descriptions are still important for 2 main reasons:
- Meta descriptions give the reader a short summary of what they can expect to find by clicking on your result.
- Meta descriptions can boost your organic CTR (Click-Through-Rate).
Think of your meta description like your Facebook ad copy, it’s role is to entice readers to click on your result.
You can get readers to click on your results by creating meta descriptions that are descriptive and that contain your target keywords and/or variations thereof.
Now that doesn’t mean you should be stuffing your meta description with your target keyword(s).
Instead, you should create keyword-rich meta descriptions, but that read in a natural, non-spammy way. Remember, meta descriptions aren’t for the search engine crawlers, they are for the humans who will be reading your content.
Here are some meta description best practices:
- Don’t make use of duplicate meta descriptions on different pages. The meta descriptions on each page should be unique.
- Write creative meta descriptions and that stand out from the competition.
- Try to keep your meta descriptions up to 160 characters. Google usually cuts off meta descriptions that are longer than 160 characters.
Image Optimization
Adding images and other visual elements to your content is essential to keeping your readers captivated and engaged with your content.
Just imagine reading a blog post without any images!
It’s important that you optimize the images in your content so that they don’t slow down your website loading speed (more on that later), provide better accessibility, and give context/descriptions to search engine crawlers.

Image source: Volusion
You can do this by making use of image alt tags. Image alt tags serve 3 main purposes:
- Screen readers read alt attributes out loud to give visually impaired users a better understanding of the images being displayed.
- If an image file can’t be displayed, the web browser will display the alt attribute in place of the image.
- Alt tags provide image descriptions and context to help search engine crawlers understand and index an image.
Making use of alt tags could also assist with image SEO. Alt attributes give you the ability to include your target keywords in another part of your content.
You must avoid stuffing your target keyword in every image alt tag in your content. Google will surely penalize you if they notice that you're stuffing keywords.
The best practice for adding image alt tags is to create alt text that describes the image and that includes your target keyword or phrase.
Now, I know creating image alt tags can take some time and seems like a tedious process, but luckily there are AI tools that you can use to automate this process completely.
AltTextGenerator is a free instant AI alt text generator that you can use to automatically generate high-quality alt text for images using advanced artificial intelligence.
Simply upload your image and the tool create SEO-optimized alt text for the image that you added.
Optimize URLs for On-Page SEO
One of the other facets of improving your site’s on-page SEO is creating SEO-friendly URLs.
We already know that a great user experience is the most important aspect of SEO. Using a logical URL structure will make your website easier to navigate, ultimately resulting in a great user experience.
Example of a logical URL structure:
www.domain.com/product/iphone
www.domain.com/blog/best-iphone-cases
Both of these examples give the user a clear idea of where he/she is on the website.
Furthermore, you’ve got to create URLs that are easy to read, short, simple to understand, and that contain the keyword that you’re targeting.
For example, the URL www.seoptimer.com/seo-crawler/ is SEO friendly because it is short, simple, and conveys what the information on that webpage is all about.
Compare that domain to www.mydomain.com/index.php?id_wcs=87570. This second domain is not SEO-friendly at all and it’s really difficult to understand what that webpage will be about.
You can also remove stop words such as for, as, in, the, and, etc. in your URLs. By doing this, you will make your URLs shorter and easier to remember.
Optimize PageSpeed
Page loading speed is a major on-page SEO ranking factor and Google has given much more weight to this metric recently.
Google more specifically measures time to the first byte, which is the time it takes your browser to receive the first byte of information from the server.

Image source: SpeedBoostr
According to Google, the ideal site speed is anything under 3 seconds.
Not only does Google like websites that load fast, but a fast-loading website also tends to do much better at creating a great user experience. Pages that have a long loading time usually have higher bounce rates and lower average time spent on page.
So then, how can you boost your page speed and make your web pages load even faster?
Move to a Faster Host
When starting, most people choose the web hosting that is the cheapest. However, choosing cheaper hosting services and packages aren’t always the best for page seed.
According to Backlinko’s analysis of 5.2 million websites, webmasters can improve a site’s loading speed by moving to a faster host.
Compress and Minify HTML, CSS and Javascript Files
By reducing the size of your CSS, HTML and Javascript files, you can reduce the overall page size. The smaller your files, the faster your pages will load.
You may be thinking that compressing website files is a challenging task, but it’s actually one of the easiest ways to reduce page load time.
You can use a tool like GNU Gzip to compress the size of your website files.
Minifying a file is the process of removing unnecessary spaces, commas and characters in your website’s code. Minification of CSS, HTML and Javascript can drastically boost page loading speed.
Compress Image Files
Large images can have a negative impact on page speed. Therefore, you should make sure that all the images on a page aren’t larger than they need to be and that the images are in the right format. It is believed that PNGs are better for graphics, whereas JPGs are better for photographs.

Image source: Reviews On Top
A word of caution, don’t use Gzip on image files. Instead, you should compress image files using an image compression tool such as TinyPNG or CompressPNG.
Make Use of Browser Caching
Browser caching is the process of storing web elements in temporary storage.
So the first time someone comes to your website their web browser has to load all the website files like stylesheets, HTML, images and javascript before accessing the page. All of the website files are stored in a cache.
But when the same person comes back to view your page a second time, only a few of the website files have to be loaded.
Use a CDN
CDNs are great for websites that experience high levels of traffic. A CDN caches your website files on a global network of servers. When a user wants to access your website, the CDN will route the request to the server that is the closest to the user.
The information that the user receives is exactly the same as the origin server, but it just loads much faster than it would if the browser requests to access a website to a server that is geographically far away.
If you want to use a CDN, a popular option is Cloudflare.
Internal Linking
What is internal linking?
Internal linking is the process of creating links from one page on your website to another page on your website.
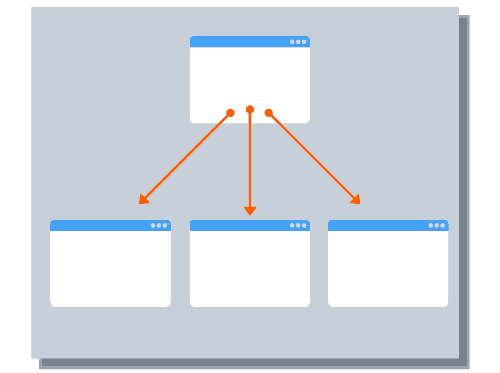
Image source: Kevin Indig
Creating internal links helps Google find, index and understand all of the pages on your website. Additionally, the more links that a page or a blog post receives, the more Google will view it as something of “high value”.
Internal linking also helps readers to find and discover other pieces of content and different pages on your website.
Internal Linking Best Practices
Always use keyword-rich anchor text
Anchor text is the clickable text in your content. These texts help Google and readers understand what the page you’re linking to is about. Just remember to avoid using the same anchor text all throughout your content, this is the same as keyword stuffing and it could lead to Google penalizing your website.
Add internal links at the top of the page to improve on-page SEO
By adding internal links high up on your pages, you will increase the time spent on your site because it gives your readers something to click on as soon as they land on your page. This is good for SEO because Google keeps track of the time that readers spend on your site and /or content. If Google notices that readers are “dwelling” on your content, they will push your results up a few spots.
Link from high-authority posts to articles that need a boost in traffic
You can do this by finding your top-ranking blog content. Then you’ll want to link to the article(s) that you’d like to boost from within the high-authority content.
On-Page SEO Myths
Google's ranking algorithm has changed so drastically over the years that SEO is an ever-changing game.
Here are some common on-page SEO myths that may have worked in the past, but that aren’t really effective anymore in today’s modern search environment.

Image source: BeaconCom
Excessive Keyword Usage is the Key to Good SEO
The days of bombarding a page with your target keyword(s) are over. Sure, in the past you could easily stuff a page with your target keyword and get away with it by appearing on the first page of the SERPs.
But Google has gotten a lot smarter over the years and they actually penalize websites that practice keyword stuffing.
Instead, Google now rewards sites that satisfy the user’s search intent in a way that is more natural-sounding.
Keywords have to Match Exactly
In the past, webmasters had to make use of exact match keywords in the content, headings, and titles on their websites to rank for certain keywords. This was before Google had an understanding of semantic search.
After the Hummingbird update in 2013, Google was able to do a much better job at matching search queries to more relevant results. The Hummingbird update helped Google in understanding search context and intent.

Image source: Search GNext
In 2015, Google introduced Rankbrain, an element of Google’s core algorithm that uses machine learning to match search queries to relevant results. By using machine learning, Google can determine the true intent of the user. Rankbrain gives Google the ability to deliver even more accurate results than with the Hummingbird update.
Because of these updates, content creators and webmasters can now make use of keyword variations, synonyms, stop words, and long-tail keywords without having to worry about missing out on traffic.
H1 is the Most Important Element on a Page for SEO
H1 tags are important, but they're not the most important element on a website or in a piece of content.

The role of the H1 tag has greater significance on providing a good overall user experience than on improving SEO rankings.
So then what is the most important element on a page? According to the Moz search ranking factors survey, title tags, also known as heading tags, are listed as the second most important ranking factor.
The on-page content is the most important ranking factor.
Content that satisfies the user's search intent is extremely important to the search engine because that is what solves the searcher’s problem.
Good content is much more beneficial to search engine rankings than H1 tags. Therefore, focus on creating content that is linkable and that fulfills search demand.
Having Lots of Backlinks is More Important than Quality Content
Sure, backlinks aren't an on-page SEO factor, but content is. And you may be asking the question:
“If I had to choose between working on backlinks or content, which one do I pick? Which one will be most beneficial to my search rankings?”
The simple answer is content.

The reason for this is that content will give other websites a reason to link back to you. Without good content, why would another website want to link back to your site?
If you focus on building a ton of links but have no quality content, then you can’t expect others to link back to you.
Remember, good content is king.
Brian Clark, the founder of Copyblogger, states that:
“The content and the value have to be there first.”
Another reason why content is more important than backlinks is because content gives the user a clear idea of what the page is all about. Backlinks, on the other hand, only give a slight indication of what the on-page content is all about.
HTTPS is Not Important
Google most definitely uses HTTPS as a ranking signal.

Image source: GlobalSign
Remember, it’s Google’s goal to provide a good user experience to its users. If a site seems unsafe to use, then that would lead to a bad overall user experience. Based on this, it only makes sense that Google favours websites that are secure, trustworthy and certified.
Just by having a look at all of the results on the first page of Google, you will notice that all of them have got HTTPS enabled.
This should serve as a clear indication that HTTPS can no longer be ignored as a ranking factor.
Now that we’ve uncovered some of the on-page SEO myths, let’s have a look at how you can improve your on-page search engine optimization.
SEOptimer On-Page SEO Checklist
Download our free on-page SEO checklist to help you boost your organic rankings in the search results.
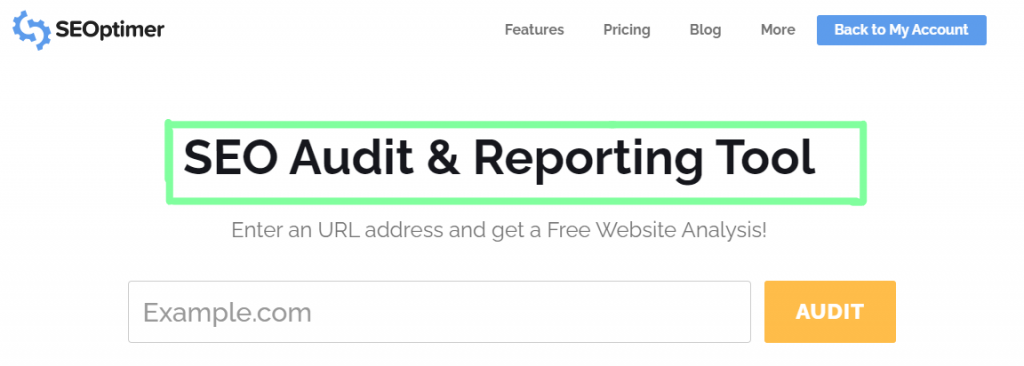
If you’d like to automatically analyze all of the above-mentioned on-page SEO factors, try our SEO audit and reporting tool.
You can use our tool to instantly check for keyword consistency, title tags, image alt tags and all the other on-page SEO factors mentioned in this article.



Conclusion
On-page search engine optimization is super important if you want to rank high in the SERPs.
By implementing these on-page SEO tactics along with off-site SEO such as link-building and guest blogging, you will boost your rankings in the search engines significantly.
We hope you found this on-page SEO guide useful and insightful. Which of these tactics are you doing to implement on your site?